First look at the new settlement rule of Australia’s electricity market, has it worked?

Photo credit: Per Bengtsson, shutterstock.com
You might not realise this when you flick your switch at home, but Australian electricity generators are forever locked in a bidding war. They compete for the right to supply electricity on the spot market. The cheapest bids win and electricity from those generators is supplied, or “dispatched”, to the grid in five-minute intervals.
This means that every five minutes, the electricity grid is rebalanced to ensure supply meets demand. Too little supply causes blackouts; too much causes tripping (and more blackouts).
But until recently, the price paid for wholesale electricity (the settlement price) on the Australian National Electricity Market (NEM) was averaged over six five-minute intervals (30 minutes). (Australia is unusual in this regard. Many grids elsewhere such as in Europe operate forward or day-ahead markets, where supply is planned in advance.)
That worked fine in the early days, but when supply started to fluctuate more wildly with the advent of intermittent renewable energy, so did the bidding war. Some generators starting gaming the system, pushing prices sky-high. Retailers complained.
So when the NEM finally introduced five-minute settlement in October 2021, it was a big deal. There was a great deal of excitement. Most commentators expected wholesale electricity prices to settle down, coal to lose market share, and batteries to boom. That’s mainly because the new system would be more efficient, rewarding cheap, nimble and flexible generators including batteries.
But what actually happened? Our analysis reveals the average spot price went up, not down, in Tasmania, Queensland, and New South Wales. Black coal-fired generators made more money on the spot market, not less. Flexible generators, especially batteries, did well too. (In the other NEM states, South Australia and Victoria, there was no significant change).
We argue further changes are needed to achieve the desired effects. These include increasing competition in the market (reducing the power of the three biggest electricity generators), building the infrastructure needed to support a green grid, and investing in more flexible and fuel-efficient technologies.
Greening the grid

Photo credit: DisobeyArt from www.shutterstock.com
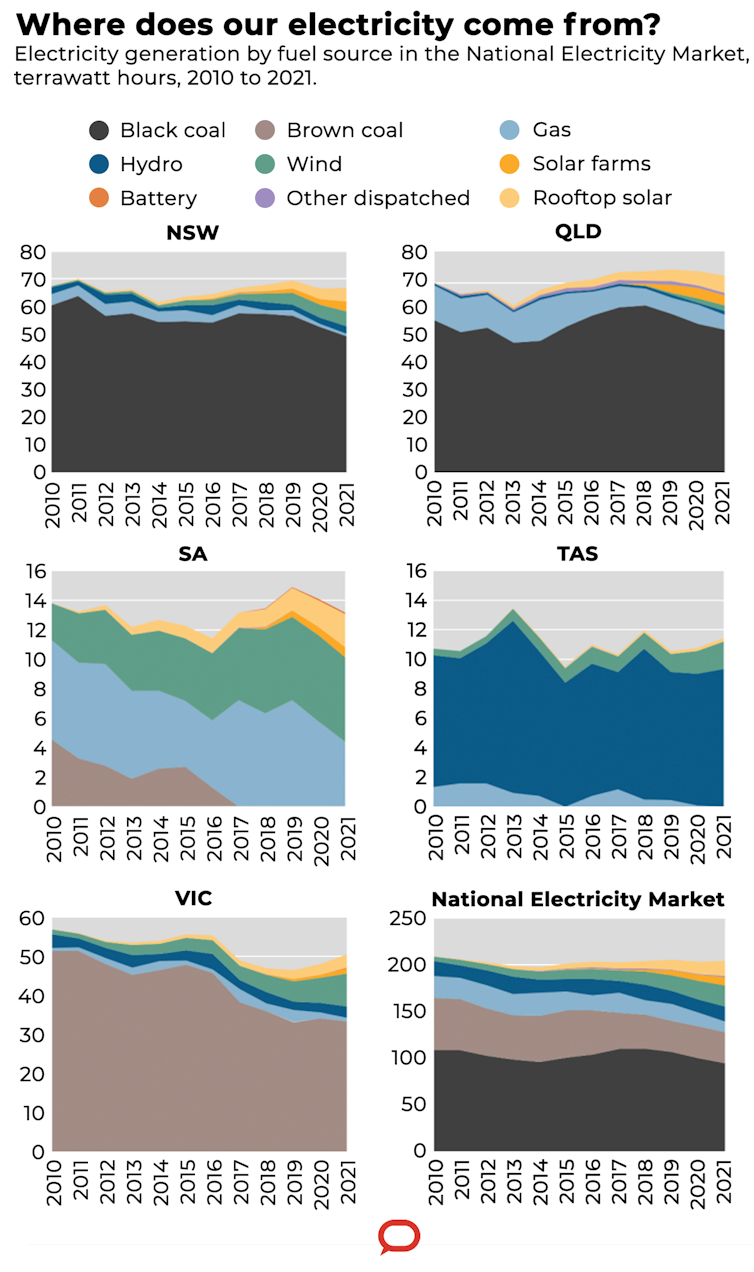
The National Electricity Market is transitioning fast to renewable energy generation to meet Australia’s 2030 emissions reduction target.
The NEM opened in 1998. The market adopted a 30-minute settlement rule at the time, because five-minute settlement would have pushed the limits of metering and data-processing capabilities.
But as the share of renewable energy grew, it became increasingly apparent that more flexible technology would be needed to cope with intermittent solar and wind power.
Problems included frequent price spikes, blackouts, power tripping, and “gaming” behaviours by major generators.
Energy retailers became frustrated by this gaming behaviour in particular, and complained to the authorities, prompting the rule change. Previously, coal and gas generators could send dispatch prices through the roof in one interval, so that when prices were averaged over the 30 minutes, it made the final trading price high. One way of doing this was to create artificial scarcity of supply, by withdrawing generation to raise spot prices.
When a price spike occurred, generators would then pile in by offering a lower price for the remainder of the 30-minute settlement period.
Five-minute settlement aimed to resolve these issues and better support the integration of wind and solar power into the electricity grid, ultimately making electricity more affordable for customers.
The new rule would also encourage investment in faster response technologies such as batteries.
Our study adds to the understanding of early effects of this regulatory change in the NEM. This will support the transition to clean energy generation, and inform policy for future electricity markets that offer stability, security and lower prices. We also propose courses of action to facilitate more effective adaptation to the rule change.
Did the new rule work?
The market had four years to prepare for the rule change, allowing generators to adjust their operations.
When five-minute settlement came in on October 1 2021, there was no substantial immediate effect.
However, within the first eight months of the change, the market started to adjust. We found that five-minute settlement led to an average spot price increase (not decrease) in Tasmania, Queensland and New South Wales.
That’s because generators no longer had a financial incentive to rebid at a very low price after a price spike, as they had done in a 30-minute trading interval. That was a strategy that caused significant fluctuation in the spot price.
Promisingly, the implementation of five-minute settlement had no measurable impact on the intensity of electricity price fluctuations. That suggests the new rule may have been effective in maintaining price stability.
So, in these early stages of the rule change, wholesale electricity customers are actually paying more, but the price has been more stable.
The impact on retail prices remains uncertain. The retailers’ costs of buying electricity and managing price risks are one component of what costumers pay in their energy bills. In 2020–21, it accounted for about a third of their bill. So if these effects persist, there is a possibility these higher prices will be passed on to consumers as well.
We also found that variable and flexible generators, especially batteries, took advantage of their flexibility to capture more revenue from the spot market. Gas generators’ revenue barely changed, but that could be because less flexible gas generators are lumped in together with highly flexible gas generators.
Surprisingly, the revenue earned by black coal-fired generators also increased. We suspect generators changed their operations and bidding strategies to align with the five-minute settlement rule. However, revenue for coal-fired generators is still likely to fall over the medium to long term.
AGL Macquarie, which includes the Liddell and Bayswater power stations shown here, is one of the largest electricity producers in Australia.
Three ways to improve five-minute settlement
It will take time to see the full effect of the rule change on the wholesale and retail electricity markets. However, we think the following changes are needed to fully realise the benefits of five-minute settlement:
- Market concentration. The NEM is a concentrated market. The three largest generators, AGL Energy, Origin Energy and Energy Australia, hold a substantial market share. Together, they supply about 80% of the generated energy. Policies that promote competition are key to realising the benefits of five-minute settlement.
- Supporting infrastructure. Five-minute settlement is expected to increase the operational cost of generating coal-fired power. That’s because ageing power plants would need to be upgraded to be able to compete during periods of fluctuating demand. Renewable generators, on the other hand, have extremely low operating costs, largely due to having no fuel costs. Coal-fired generators are likely to lose revenue and leave the market much earlier than expected. Firming and flexible demand technologies such as energy storage systems (pumped hydro, batteries or solar thermal) can effectively respond to the new market conditions and fill the gap.
- Fuel-efficient and flexible technologies. Technologies such as batteries, pumped hydro and aero-derivative gas turbines operate more effectively in a five-minute settlement design. The recent rise in gas prices also necessitates investment in flexible and fuel-efficient technologies, such as reciprocating gas engines.
Without policies to address these three areas, we believe five-minute settlement is unlikely to offer substantial benefits to the market.![]()
SSRN/Australian Energy Regulator
Christina Nikitopoulos, Associate professor, Finance Discipline Group, University of Technology Sydney and Muthe Mwampashi, PhD Candidate, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

